Google has devised a set of guidelines to provide a framework that serves to provide consistency in its approach to ranking. The recommendations aim to improve the quality of Google’s search function and offer users an improved search experience. The Quality Rater Guidelines serve as a reference for quality raters performing random checks to verify that the websites displayed in the search results are relevant to help users. According to Search Engine Journal, ratings by quality raters do not impact the ranking of a particular site but help collectively improve Google’s algorithm.
Evaluation Criteria Specified in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines
Page Quality: Three things are involved; website purpose, quality of the content, and “Expertise”, “Authoritativeness”, and “Trustworthiness” demonstrated by the website. It is especially vital for websites in the YMYL space because health and finance are sensitive issues for users.
Content evaluation: Google recommends that quality raters should concentrate on the website’s main content and assess its quality for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EAT). The second focus must be the elements comprising supplementary content, like navigation. The third area of focus deals with website monetization, like advertisements. These elements are negative, only when they interfere with the main content. For sites to rank high, they should have a high level of EAT, main content of high quality, user-friendly navigation, good website reputation, and transparency regarding the identity of the source of the content.
Latest Changes to Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG)
The foremost aim of Google Quality Rater Guidelines is meeting user needs, which is the reason for the guidelines to keep evolving, with Google issuing updates as and when it feels the need to. The latest changes, made in December 2022, have significantly changed the document structure and added several new sections and tables. Some of the most important changes include:
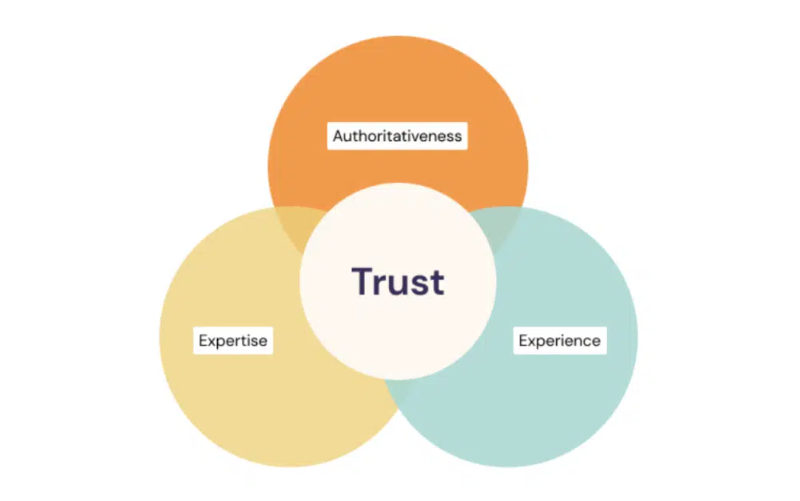
EEAT introduced: While Google has always placed great importance on the principles of Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EAT) for evaluating the worth of a website and its rank, it has now extended the concept by adding “Experience”. It means that from now Google will give a better rank to websites with content crafted by creators with first-hand experience in the subject. Despite the reframing of EAT, Google has gone on record that ‘Trust” remains the fulcrum of the concept and is the “most important member of the E-A-T family.” The updated guidelines also provide information on concepts, like website and content contributor reputation evaluation, the extent to which E-A-T is significant, how users should evaluate them, what harmful content means, etc.
More inclusive stance: Google seems to have modified the language used in its guidelines to keep up with the times by being more inclusive. To this extent, it has included many more mentions of influencers, social media, and different forms of content like UGC, video, and social media posts. Google has also adopted a granular approach to answering many common queries about the functioning of EAT and the extent it is important for different subjects. The revised guidelines also specify what constitutes harmful content and whether it is adequate for content creators to rely on everyday experience to produce reliable content on any subject.
Understanding the website: Google has also updated its guidelines for identifying the person or entity operating the website. It has asked its quality raters to find out who is responsible for the website and its content creation and try to look for the same information on the website. It is the first time Google has extended the reputation of the website to refer to the reputation of the people responsible for the website and the content. Google has also stated that raters may accept aliases or usernames to identify the content creator for content on website forums and social media where the creators have not shared personally identifiable information.
Page quality rating: While Google has changed the order of some of its recommendations relating to rating the quality of pages and analyzing information on reputation, it also offers a new process for evaluating page quality. The three-step process comprises assessing the real purpose of the web page and establishing how deceptive or harmful it is, evaluating the possibility of the page causing harm, being spammy or untrustworthy. While raters should give the lowest quality assessment to untrustworthy, spammy, or harmful pages, however, for pages not deemed harmful, they should also base their quality rating on how well the page attains its purpose.
YMYL content: Google has also asked its raters to keep in mind the degree of YMYL content on the website based on its potential to cause harm to users. Google retains its focus on the importance of the YMYL content aligning with expert opinions and being factually accurate.
Website type: Google has introduced consideration for understanding the website type. It asks raters to classify websites based on whether they are corporate or hobby websites, involves financial transactions, or require users to make payments, whether professional support them or volunteers, etc. It deems the classification necessary because users have different expectations of page quality from different website types.
Main content quality: Google has made significant changes to its recommendations to raters for assessing the quality of the main content of a page. While earlier Google had stated that for creating high-quality main content, you need to invest significantly in “time, effort, expertise, and talent/skill”, it has now added the word “originality”, and removed “time”. It has also added a new table to this section that outlines the process of assessment of page quality. Google is also emphasizing the amount of effort as a consideration factor for judging page quality. It focuses on the originality of content and the presence of subject insights not found on other online resources.
Conclusion
Apart from being valuable to Google’s quality raters, the guidelines provide helpful direction to people wanting to understand the focus of Google’s search algorithm. According to Pittsburgh Internet marketing service experts, in addition to what the guidelines mention specifically, it can also help to read between the lines of the guidebook to know and understand what Google is looking for in terms of EEAT, user experience, and content quality. It will help to get better search engine rankings and avoid algorithm updates negatively impacting you.

The Search Engine Cage team is on a mission to educate entrepreneurs. We make things easier for the small business owner, by writing articles that help them to understand SEO and Digital Marketing.